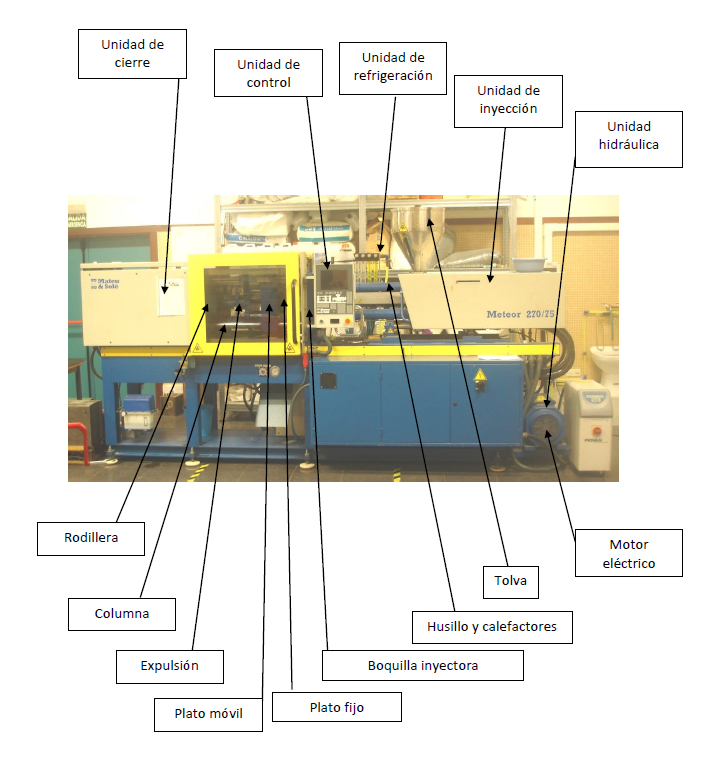
Each part of the machine plays a specific and essential role in the injection process, ensuring the quality and compliance of the final products. This article offers a detailed overview of the key components of a plastic injection molding machine, explaining their function and importance in the manufacturing process.

Clamping Unit
The clamping unit is one of the fundamental parts of the plastic injection molding machine. Its main function is to ensure that the mold remains closed under pressure during the injection process. This is achieved through a clamping force system that can be hydraulic, mechanical, or a combination of both. The accuracy of the clamping unit is crucial to prevent any leakage of molten plastic material and to ensure that the molded piece has the desired shape and size. Additionally, the clamping unit is responsible for opening the mold once the plastic has cooled and solidified, allowing for the removal of the finished piece.
Control Unit
This unit manages and monitors all the machine’s functions, from temperature control to injection speed and clamping pressure. Through the use of computerized control systems, it is possible to make precise adjustments that directly affect the quality of the final product. These systems allow injection technicians to set specific parameters for each injection cycle, thus ensuring consistency and repeatability in the production of plastic parts.
Cooling Unit
The cooling unit in a plastic injection molding machine plays a crucial role in mold temperature control. This unit uses a cooling system, typically based on water or oil, to dissipate the heat generated during the injection process. Effective temperature control is essential to ensure that the plastic cools and solidifies at an optimal rate, which is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity and dimensional tolerances of the molded piece. Moreover, an efficient cooling system can significantly reduce cycle times, increasing production efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Injection Unit
The injection unit is the component of the machine responsible for melting the plastic and injecting it into the mold. This unit consists of a screw or plunger that rotates within a heated barrel, melting and mixing the plastic as it moves towards the injection nozzle. Precision in temperature control is vital to ensure that the plastic reaches the correct viscosity.
Hydraulic Unit
Plastic injection molding machines often employ hydraulic systems to generate the movement and force required in different parts of the machine, such as the clamping unit and the injection unit. The hydraulic unit, composed of pumps, valves, and hydraulic cylinders, provides the power for these movements.
Toggle
The toggle is a typical mechanism in plastic injection molding machines, particularly in the clamping units. Its function is to convert the linear motion of the hydraulic piston into the mold’s opening and closing movement. This mechanism is valued for its ability to apply a high clamping force to the mold.
Tie Bar
The tie bars are fundamental structural elements in the machines. They provide stability and precise alignment between the movable and stationary plats. During the injection process, the tie bars guide the movement of the movable plat while the clamping force is applied, ensuring that the mold closes uniformly and precisely. The rigidity and strength of the tie bars allow for maintaining the structural integrity of the machine under the large forces involved. Additionally, the distance between tie bars is determinant in establishing the dimensions of the mold, as molds exceeding this distance would not be usable with this machine.
Movable and Stationary Plats
In the plastic injection molding machine, the movable and stationary plats are the surfaces to which the two halves of the mold are mounted. The stationary plat is in a fixed position, while the movable plat slides along the tie bars to open and close the mold. These plats not only support the mold but also ensure its precise alignment during the process.
Injection Nozzle
The injection nozzle is the part of the machine that connects the injection unit with the mold. It is responsible for directing the molten plastic from the screw of the injection unit into the mold cavities. The nozzle must seal properly against the mold’s injection plate to prevent material leaks and ensure efficient injection. The design of the nozzle, as well as its maintenance, are essential to avoid issues such as clogging or overheating, which can negatively impact the quality of the injected product.
Screw and Heaters
The main function of the screw is to melt and homogenize the plastic material, in addition to pushing it towards the injection nozzle. The screw rotates within the injection barrel, generating heat through friction and mixing the plastic material uniformly. The heaters, composed of various resistances located around the barrel, complement this process by providing the additional heat needed to maintain the plastic in its molten state.
Hopper
The hopper is the component where the plastic material is stored before its introduction into the injection unit. This element ensures a constant and controlled flow of material towards the screw. Some hoppers include drying devices or mixing systems to prepare the material before processing, ensuring that the plastic’s properties are as desired.
Electric Motor
The electric motor is the main source of energy that drives the mechanical components of the injection molding machine, such as the screw and the clamping system. These motors are usually high efficiency and controlled by computerized systems to optimize energy consumption and the precision of movements. For a graphical aid, below are indicated the different parts of an injection molding machine from Mateu & Solé with the denomination 270/75.